Mastering the Basics of Nouns – Their Categories, Functions, and Usage in English Language
Understanding nouns, their types and functions is the crux of English grammar, for what can we do without nouns. Little wonder that nouns are given the first place among the parts of speech. They’re like the strong foundation of a building, helping us put our sentences together in a way that makes sense. From something we can touch, like an “apple” or a “book,” to something we can feel, like “justice” or “love,” nouns cover everything we experience.
Moreover, in our chats with friends or family, nouns pop up all the time, and make our conversations flow smoothly. Imagine how sentences would appear if there were no nouns to name the characters, places and feelings! In stories and books, nouns get even more interesting because they carry lots of different meanings that make the story richer. Nouns come in all sorts – like everyday ones we use all the time, and special ones that stand out, like names of places or people. There are also nouns that talk about groups of things or ideas we can’t touch. As we Explore all these types of nouns, we see just how awesome and powerful they are in shaping how we talk and understand the world.
Understanding Nouns
Before we dive into types and functions of nouns, let me take you through the basic meaning.
What is a noun?
A noun is a name given to anything. The word assigned to a person, animal, place, thing or abstract idea is called a noun. In a simple language, a noun is a naming word.
|
Person |
Animal |
Place |
Thing |
Abstract |
|
Tina |
lion |
Lagos |
pen |
happiness |
|
Cynthia |
cat |
Nigeria |
table |
judgement |
|
girl |
goat |
Ghana |
bag |
joy |
|
teacher |
pigeon |
Ibadan |
food |
anger |
|
doctor |
frog |
London |
television |
freedom |
|
Mercy |
cheetah |
Port Harcourt |
pot |
identity |
|
man |
antelope |
Maryland |
wall |
love |
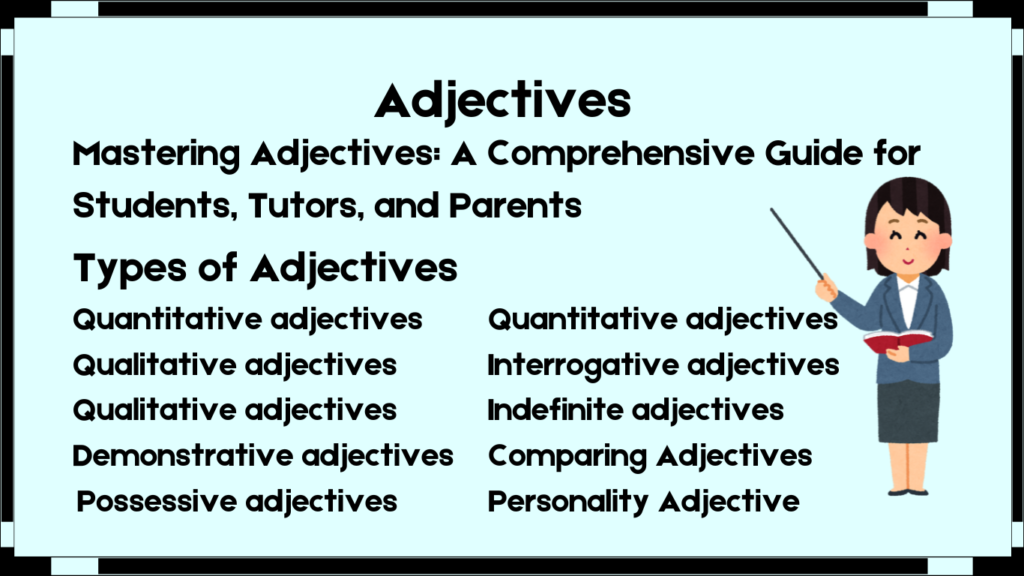
Types of Nouns
Understanding the types of noun is fundamental for correct usage. I have dedicated this section to providing a comprehensive guide to the types of noun, keeping it simple and illustrative to aid understanding.
A noun can be classified into:
-
Proper Nouns
-
Common Nouns
-
Concrete Nouns
-
Abstract Nouns
-
Collective Nouns
-
Countable Nouns
-
Uncountable Nouns
In this section, we are going to explore these categories of nouns with examples.
-
proper noun
What are proper nouns?
Proper nouns are special naming words. They are special names assigned to persons, places, pets, or things and they are always capitalized. They help us to distinguish unique entities from their general counterparts. Examples include “Banana Island,” “Amanda Johnson,” “River Niger” and “The Mona Lisa. Some proper nouns are concrete in nature since they can be seen and touched. Proper nouns can also be abstract, such as names of :
– Concepts (Independence, Justice)
– Religions (Christianity, Buddhism)
– Theories (Gravity, Evolution) – when used as proper nouns Example: Gravity is my favorite album by John Mayer. Gravity Sports offers top-notch climbing gear.
Proper nouns at a glance
|
Person |
Pet |
Thing |
Organza ton |
Days of the week |
Months of the year |
Title of book |
|
Tina |
Hansel |
Toyota |
Emerald school |
Monday |
January |
Cerebella |
|
John |
Bingo |
Peugeot |
The church of God |
Tuesday |
February |
Little red Riding Hood |
|
Jane |
Subby |
Corolla |
Life’s Good |
Wednesday |
March |
Sugar Girl |
|
Jim |
Max |
Mercedes Benz |
National Drug Law Enforcement Agency |
Thursday |
April |
The Joy of Motherhood |
|
Joel |
Buc |
Jeep |
Zenith Ban |
Friday |
May |
Patina |
|
Lois |
Doss |
Land Rover |
First Ban of Nigeria |
Saturday |
September |
Cinderella |
|
Arielle |
Archer |
Nissan |
Four Mills of Nigeria |
Sunday |
December |
Purple Hibiscus |
-
Common noun
What are common noun?
Unlike proper nouns which are unique names, Common nouns are names given to things of the same kind. For example, every little female is called a girl. Every adult female is called a woman, and every adult male is called a man. Examples of common nouns are: girl, boy, teacher, doctor, chair, pen, child, adult, church, school, dog. Common nouns are concrete if they can be seen and touched. They are abstract if they can’t be seen and touched.
Here are some examples of abstract common nouns:
– Emotions: happiness, sadness, anger, fear, love
– Concepts: freedom, justice, peace, hope, democracy
– Ideas: thought, imagination, creativity, inspiration, motivation
– Feelings: joy, sorrow, excitement, boredom, nostalgia
– Phenomena: time, space, energy, gravity, chaos
Relationship between common nouns and proper nouns
To illustrate the relationship between proper nouns and common nouns, let me put it this way: “Girl” is a common noun, but the particular name of the girl, such as “Sophia”, is a proper noun. “Dog” is a common noun, but the particular name of the dog, such as “Max”, is a proper noun. “Teacher” is a common noun, but the particular name of the teacher, such as “Ms. Johnson”, is a proper noun. This is illustrated in the table below
Common and proper nouns at a glance
|
Common noun |
Proper noun |
|
girl |
Tina |
|
boy |
John |
|
teacher |
Mr. Peter |
|
doctor |
Dr. Allen |
|
school |
Emerald School |
|
dog |
Subby |
|
car |
Toyota |
A noun is ether concrete or abstract.
-
Concrete Noun
What are concrete nouns?
Concrete nouns are nouns that are physically present. They appeal to the senses, especially sight and touch. You can see and touch them. Think of the things you can see, hold, and perceive through your senses. They are called concrete nouns. Concrete is the opposite of abstract. Examples are “spoon,” “sand,” “boy,” “love,” and “house”
-
Abstract Nouns:
What are abstract nouns?
In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are non-physical concepts, qualities, or states. They cannot be perceived by the senses. They represent ideas, emotions, or conditions that exist beyond physical reality. Examples include “boldness,” “independence,” “justice,” “love,” and “goodness”
How Abstract nouns are formed
Abstract nouns can be derived from verbs as shown in the table below.
|
Verb |
Abstract Noun |
|
see |
sight |
|
die |
death |
|
plant |
plantation |
|
deliver |
deliverance |
|
forgive |
forgiveness |
|
try |
trial |
|
breathe |
breath |
|
bathe |
bath |
|
clothe |
cloth |
|
bribe |
bribery |
|
accept |
acceptance |
|
admire |
admiration |
|
adore |
adoration |
|
appear |
appearance |
|
appreciate |
appreciation |
|
believe |
belief |
|
accomplish |
accomplishment |
- Some abstract nouns are made from adjectives. Below are abstract nouns derived from adjectives
|
Adjectives |
Abstract Noun |
|
strong |
strength |
|
generous |
generosity |
|
bold |
boldness |
|
warm |
warmth |
|
beautiful |
beauty |
|
long |
length |
|
weak |
weakness |
|
lucky |
luck |
|
absent |
absence |
|
sad |
sadness |
|
present |
presence |
|
hot |
heat |
|
reliable |
reliability |
|
protective |
protection |
|
wide |
width |
|
mad |
madness |
|
stubborn |
stubbornness |
-
Collective Nouns:
What are collective nouns?
Collective nouns are used to talk about groups of people, animals, or things as one entity. They refer to a collection of individuals or objects treated as a unit. Examples include “team,” “herd,” “flock,” “family,” and “audience.”
A band of musicians
A class of students
A bevy of lades
A board of directors
A bunch of bananas
-
Countable:
Countable noun describes nouns that can be counted or numbered. When you can refer to a noun as singular or plural, it means the noun can be counted.
Example:
|
singular |
plural |
|
One cup |
Two cups |
|
One person |
Ten persons |
|
One dog |
Five dogs |
-
Uncountable Nouns:
What are uncountable nouns?
Uncountable is a term that describes nouns that cannot be counted. This kind of noun cannot be described as singular or plural since they cannot be counted. Examples are water, rice, juice, sand, and money. However, when these nouns are measured, they become countable. Examples: one cup of rice, two cups of rice. One glass of water, four glasses of water.
Functions of Nouns:
Beyond their classification into various types, nouns serve several essential functions within sentences.
- Subject: Nouns often function as the subject of a sentence, performing the action described by the verb. For example, in the sentence “The dog barks loudly,” the noun “dog” serves as the subject.
- Object: Nouns can also function as objects within sentences, receiving the action performed by the subject. In the sentence “She read a book,” the noun “book” serves as the direct object of the verb “read.”
- Complement: Nouns may function as complements, providing additional information about the subject or object. In the sentence “He is a doctor,” the noun “doctor” serves as a predicate nominative, renaming or describing the subject “he.”
- Possession: Nouns can indicate possession or ownership when used in the possessive form. For example, in the phrase “Sarah’s car,” the noun “car” indicates something owned by Sarah.
In conclusion, nouns are the foundation of language. They enable us to communicate effectively and expressively. By understanding the various types and functions of nouns, we gain deeper insight into the structure and mechanics of language. Whether describing the tangible world around us or contemplating abstract ideas, nouns serve as our linguistic anchors. They ground our thoughts and expressions in meaningful ways. Therefore, understanding nouns is essential for language development.