Mastering Pronouns in English: A Complete Guide for Learners and Exam Takers
Mastering pronouns in English grammar is undeniably vital, yet many learners struggle to use them correctly. In this guide, I will walk you through the different types of pronouns, their roles, and provide examples to help you master them. Whether you’re preparing for an exam like WAEC, NECO, JAMB, SAT, or IELTS, or just aiming to improve your English, understanding pronouns is crucial.
What is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. They help us to avoid repetition and, they make sentences smoother. Instead of saying “John went to John’s car because John left John’s phone,” we can simply say, “John went to his car because he left his phone.” Here, he and his are pronouns.
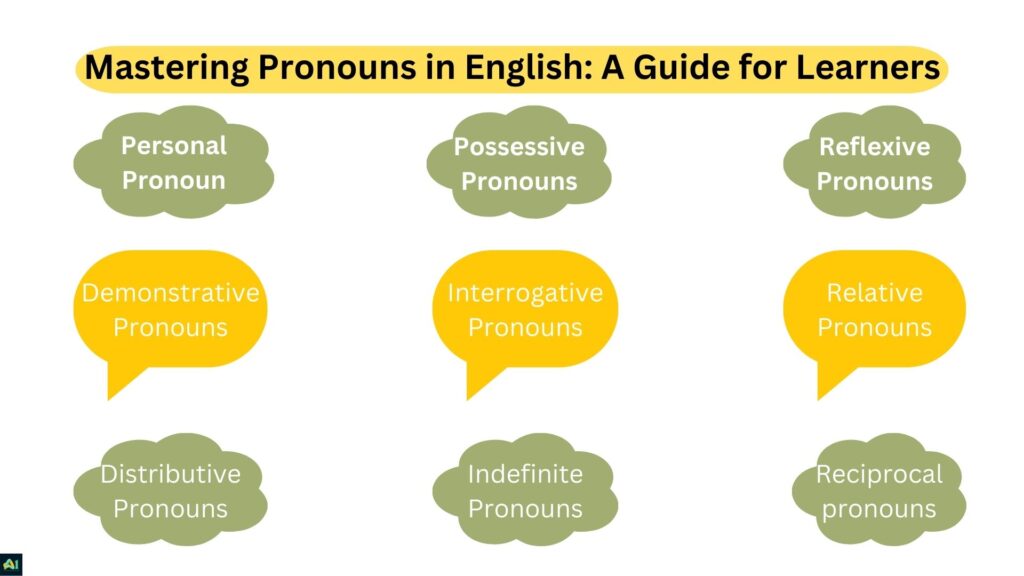
Types of Pronouns
1. Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns take the place of specific people or things. They can function as either the subject or the object of a sentence, and they are categorized as first person, second person, or third person. The form of personal pronouns changes depending on whether they are the subject or the object of the sentence. For example, “I” changes to “me,” and “we” changes to “us.”
- Subject Pronouns: These pronouns perform the action in a sentence. Examples include:
- I (first person singular – the speaker)
- We (first person plural – the speakers)
- You (second person singular and plural – the listener or reader)
- He, She, It (third person singular – the person or thing being talked about)
- They (third person plural)
Example: I am going to the market.
- Object Pronouns: They are the pronouns that receive the action of the verb. Examples include:
- Me (first person singular)
- Us (first person plural)
- You (second person singular and plural)
- Him, Her, It (third person singular)
- Them (third person plural)
Example: The teacher gave him the assignment.
2. Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns show ownership or possession. They show us that something belongs to someone or something.
- Singular: mine, yours, his, hers, its
Example: This book is mine. - Plural: ours, yours, theirs
Example: The decision is theirs to make.
3. Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of the sentence are the same, reflecting the action back on the subject. They end in “-self” for singular or “-selves” for plural forms.
- Singular: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself
Example: She taught herself French. - Plural: ourselves, yourselves, themselves
Example: We did it all by ourselves.
4. Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are used to point out the specific people, places, or things we are talking about. They can be in the singular form or plural form.
- Singular: this, that
Example: This is my favorite book. - Plural: these, those
Example: Those are beautiful flowers.
5. Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. Common examples are:
- who: It is used only for persons in the subjective case. Ex: Who is the tallest man in the world?
- whom: We use it for persons in the objective case. Ex: Whom did you invite to the party?
- whose: We use it in the possessive case. Ex: Whose car is parked outside?
- which: It is used for both animals and things. Ex: Which is the shortest way to the museum?
- what: Use it for things. Ex: What can I do for you?
6. Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns link clauses or phrases to a noun or another pronoun. They provide more detail about the noun.
- Who: used for people as the subject.
Example: The girl who saved you is my sister. - Whom: used for people as the object.
Example: The woman whom you saw at the market is my sister. - Whose: indicates possession.
Example: The boy whose father is the principal is very arrogant. - Which: used for things as both subject and object.
Example: The book which you read was applauded by everyone. - That: used for people or things.
Example: This is the pet that my friend gave me.
Example: That’s the man that had an accident.
7. Distributive Pronouns
Distributive pronouns refer to individuals or items one at a time, emphasizing that they are considered separately, even if they are part of a group. They are used when referring to every single member of a group but treating them individually.
- Common distributive pronouns: each, either, neither Examples:
- Each of the students received a prize. (Refers to every student individually.)
- Either of the two options is acceptable. (One out of two, considered separately.)
- Neither of the answers is correct. (None of the two, considered individually.)
8. Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people or things. They do not point to a particular person, thing, or amount, and they are often used when the speaker is unsure or doesn’t need to specify exactly who or what they are referring to. e.g. someone, everyone, anybody, nobody, all, some, few, many
Examples:
- Someone left their jacket here. (does not specify any particular person)
- Few of the participants showed up on time. (Refers to an indefinite number of people.)
9. Reciprocal pronouns
Reciprocal pronouns are used to talk about mutual relationships. They indicate that the members of a group are performing the same action toward each other. Common Reciprocal Pronouns are
- Each other: Used to talk about two people or things.
- One another: Used when referring to more than two people or things, although this distinction is not strictly followed in modern English. (For exam purpose you one another when referring to more than two person or things.)
Examples:
- The two sisters love each other.
(This means that the love is mutual) - The players on the team support one another during the game.
(This means that all team members support each other.)
The importance of Mastering Pronouns in English
Mastering pronouns is essential, especially in exams like WAEC, NECO, JAMB, and IELTS. These exams frequently test your understanding of correct pronoun usage and agreement. You may encounter questions that require you to correct pronoun errors or select the appropriate pronoun in multiple-choice formats. For writers, pronouns are also invaluable because they help avoid repetition and make sentences smoother.
To excel in exams and improve your writing, follow these tips:
- Understand Context: Always read the entire sentence to determine which noun the pronoun refers to.
- Practice Agreement: Ensure the pronoun agrees with its noun in both number (singular/plural) and gender.
- Review Types of Pronouns: Familiarize yourself with the different types of pronouns (personal, possessive, reflexive, etc.) and practice using them correctly.
Mastering pronouns will improve both your writing and your exam performance by ensuring precision and clarity in your communication.
Common Mistakes with Pronouns
Below are some common mistakes people often make with pronouns. Try to avoid these errors to ensure clarity in both your speech and writing.
- Mixing Subject and Object Pronouns:
Incorrect: Him and I met at the restaurant.
Correct: He and I met at the restaurant. - Ambiguous Pronoun Reference:
Incorrect: When Tim met Jerry, he told him to call later. (Who is “he”?)
Correct: When Tm met Jerry, Tim told Jerry to call later. - Overuse of Pronouns:
Incorrect: She said she would help her with her project.
Correct: Jane said she would help Maria with her project.
How to Use Pronouns Effectively in Writing
- Be Clear: Always ensure that your pronoun clearly refers to a specific noun.
- Avoid Redundancy: Don’t overuse pronouns in a sentence. If necessary, repeat the noun for clarity.
- Check Agreement: Pronouns must agree with the nouns they replace in both number and gender.
Pronouns are small but mighty components of the English language. By mastering pronouns in English, you can significantly improve your writing and speaking skills. Whether you’re working on a school assignment, studying for an exam, or enhancing your everyday communication, understanding how to use pronouns correctly will make a big difference.